Queues & Stacks
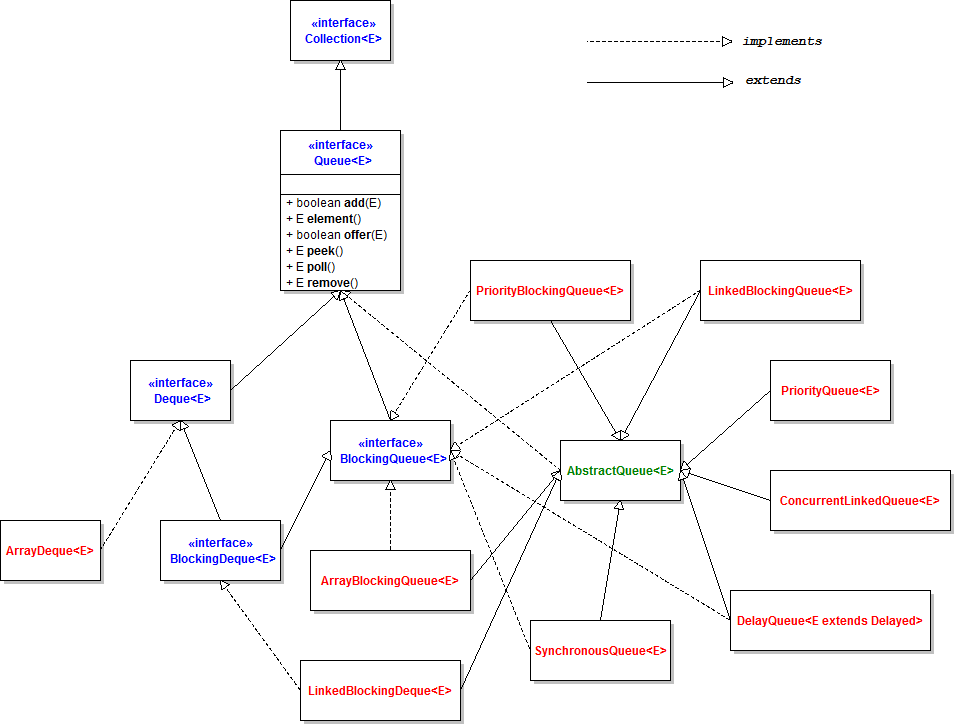
Priority Queue
//The type of the PriorityQueue is Integer.
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
//The elements are added to the PriorityQueue
queue.addAll( Arrays.asList( 9, 2, 3, 1, 3, 8 ) );
//The PriorityQueue sorts the elements by using
// compareTo method of the Integer Class
//The head of this queue is the least element with
// respect to the specified ordering
System.out.println( queue );
//The Output: [1, 2, 3, 9, 3, 8]
queue.remove();
System.out.println( queue );
//The Output: [2, 3, 3, 9, 8]
queue.remove();
System.out.println( queue );
//The Output: [3, 8, 3, 9]
queue.remove();
System.out.println( queue );
//The Output: [3, 8, 9]
queue.remove();
System.out.println( queue );
//The Output: [8, 9]
queue.remove();
System.out.println( queue );
//The Output: [9]
queue.remove();
System.out.println( queue );
//The Output: []
Deque
A Deque is a "double ended queue" which means that a elements can be added at the front or the tail of the queue. The queue only can add elements to the tail of a queue.
Creating a Deque
Before you can use a Java Deque you must create an instance of one of the classes that implements the Deque interface. Here is an example of creating a Java Deque instance by creating a LinkedList instance:
Here is another example of creating a Java Deque by creating an ArrayDeque instance:
| Method | Brief description |
|---|---|
getFirst() |
Gets the first item of the head of the queue without removing it. |
getLast() |
Gets the first item of the tail of the queue without removing it. |
addFirst(E e) |
Adds an item to the head of the queue |
addLast(E e) |
Adds an item to the tail of the queue |
removeFirst() |
Removes the first item at the head of the queue |
removeLast() |
Removes the first item at the tail of the queue |
Adding Elements to Deque
Deque deque = new LinkedList();
//Adding element at tail
deque.add("Item1");
//Adding element at head
deque.addFirst("Item2");
//Adding element at tail
deque.addLast("Item3");
Removing Elements from Deque
//Retrieves and removes the head of the queue represented by this deque
Object headItem = deque.remove();
//Retrieves and removes the first element of this deque.
Object firstItem = deque.removeFirst();
//Retrieves and removes the last element of this deque.
Object lastItem = deque.removeLast();
Retrieving Element without Removing
//Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of the queue represented by this deque
Object headItem = deque.element();
//Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this deque.
Object firstItem = deque.getFirst();
//Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this deque.
Object lastItem = deque.getLast();
Iterating through Deque
//Using Iterator
Iterator iterator = deque.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext(){
String Item = (String) iterator.next();
}
//Using For Loop
for(Object object : deque) {
String Item = (String) object;
}
Stack
Stacks are a LIFO (Last In, First Out) Data structure for objects.
Java contains a Stack API with the following methods
| Method | Description | Return Type |
|---|---|---|
Stack() |
Creates an empty Stack | void |
isEmpty() |
Is the Stack Empty? | Return Type: Boolean |
push(Item item) |
push an item onto the stack | void |
pop() |
removes item from top of stack | Return Type: Item |
size() |
returns # of items in stack | Return Type: Int |
import java.util.*;
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Stack st = new Stack();
System.out.println("stack: " + st);
st.push(10);
System.out.println("10 was pushed to the stack");
System.out.println("stack: " + st);
st.push(15);
System.out.println("15 was pushed to the stack");
System.out.println("stack: " + st);
st.push(80);
System.out.println("80 was pushed to the stack");
System.out.println("stack: " + st);
st.pop();
System.out.println("80 was popped from the stack");
System.out.println("stack: " + st);
st.pop();
System.out.println("15 was popped from the stack");
System.out.println("stack: " + st);
st.pop();
System.out.println("10 was popped from the stack");
System.out.println("stack: " + st);
if(st.isEmpty())
{
System.out.println("empty stack");
}
}
}
Blocking Queue
A Blocking Queue is an interface, which is a queue that blocks when you try to dequeue from it and the queue is empty, or if you try to enqueue items to it and the queue is already full. A thread trying to dequeue from an empty queue is blocked until some other thread inserts an item into the queue. A thread trying to enqueue an item in a full queue is blocked until some other thread makes space in the queue, either by dequeuing one or more items or clearing the queue completely
LinkedList : FIFO Queue
The java.util.LinkedList class, while implementing java.util.List is a general-purpose implementation of java.util.Queue interface too operating on a FIFO (First In, First Out) principle.